Zero trust network access (ZTNA) controls users' application and data access under the principle of zero trust – "no traffic is trusted." It may also refer to a security solution that accomplishes the same. It is highly similar to software defined perimeter (SDP) in that it controls access at the application level – but goes beyond concealing network resources within a perimeter by completely restricting access.
Why Is Interest in ZTNA Growing?
Interest in ZTNA has been increasing in recent years for several reasons, including:
Business Environment Issues Accelerated by Pandemic
Ambiguous Boundaries
The pandemic forced businesses to lock down, resulting in many white-collar employees working remotely. Employees' work in the office expanded outside those boundaries, such as at home and in public spaces. However, the concept of "boundaries" has become vague, making it difficult to control security policies. As a result, the risk of cyber attacks is increasing.
Diversification of Information Assets
The shift to remote work has moved most operations to the cloud, making web meetings, storage, chat, and more cloud-centric. Information assets previously aggregated into on-premise file servers are now distributed to public and private clouds and external storage devices. The broader scope of protection increases the burden on the system division and the risk of information leakage.
Unreliable Terminals
With the shift to remote work, bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies have increased. In many cases, employees working offsite must use multiple devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and notebook computers. These devices often have insufficient security measures, and increased access from these devices raises security risks.
Complex Risk Management
Global companies may manage gateway devices connected to internal networks at each branch, which can complicate security policy control.
Increasingly Sophisticated Cyber Attacks
Targeted Attacks
The number of targeted attacks directed at specific companies and organizations has increased. The rise in remote work environments complicates this, as vulnerable VPN gateways and personal devices are ripe for targeting. For example, at the height of the pandemic in 2020, there was a spike in Windows' Remote Desktop Protocol exploits.
Supply-Chain Attacks
Cyber criminals have not limited themselves to global corporations. They're also attacking supply chains through system vulnerabilities and malware. At the end of 2020, prominent security provider solutions faced attacks through supply chains.
Expanding Ransomware Threats
Aggressive Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is now the most formidable cyber attack, and the damage of ransomware attacks can be massive. In May 2020, the Dark Side – a criminal ransomware group – targeted a U.S. oil pipeline. The criminals exploited the VPN password authentication and were paid $4.4 million after intruding into the system. Of that amount, authorities were only able to recoup $2.3 million.
Targeted Ransomware and Dual Intimidation
Ransomware is also becoming increasingly sophisticated, with many attacks directed at specific companies and organizations. This is called "targeted ransomware," where criminals customize their attack to suit the industry they've targeted. In addition to encrypting data, they also threaten to publish stolen data if they aren't paid, which is called "dual intimidation."
RaaS
Ransomware as a service (RaaS) is a business platform for ransomware that allows ransomware providers and hackers to spread attacks. Companies need to adapt to these evolving cyber attacks and changing business environments.
Zero Trust vs. ZTNA
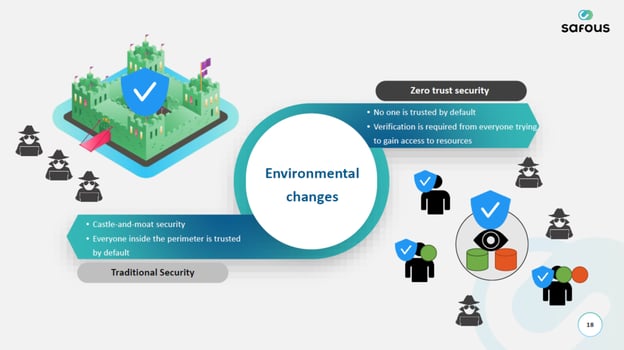
Against this backdrop, the concept of zero trust is becoming increasingly important.
What Is Zero Trust?
Zero trust is a security concept that sees all communications inside and outside the company as "unreliable." While this concept has existed since 2010, the pandemic has directed much attention to zero trust due to an increase in remote and hybrid work arrangements.
The conventional security model is called "borderline security." Boundary-type security essentially handled internal access and post-authentication access as secure. However, these concepts have limitations because the boundaries have become vague in recent years.
Why Use Zero Trust?
Risks of VPNs
VPNs have become increasingly popular with the spread of remote work, but they carry security risks. For example, if VPN credentials are leaked, there is a risk that malicious parties could access a company's information assets. Additionally, if traffic to the VPN device is concentrated, the slowed system response time interferes with business operations. The introduction of ZTNA can address the risks of using VPNs.
Diversification of Attack Targets
As already mentioned, cyber attacks are becoming more sophisticated, and their methods and targets are becoming more diverse. Every touchpoint – e-mail, SMS, suppliers, etc. – can be the starting point of an attack. Under these circumstances, zero trust becomes even more critical.
How Does ZTNA Work?

Based on the zero trust concept, network administrators control ZTNA access at the application and data level. The terminal communicates with the access point instead of the VPN gateway, suppressing the response delay due to traffic concentration. Let's break down these components in further detail:
-
Application-Level Access Control
ZTNA provides application-level rather than network-level access control. Every time an application is accessed, ZTNA evaluates the user and frees only the data they should be able to access. In the unlikely event that credentials are compromised, confidential resources are protected.
Authentication and Authorization
ZTNA enables authentication and authorization policies, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO), to be centrally managed. Centralized management of authentication and authorization policies ensures safety in various business environments.
-
Audit and Logging
Log management features are essential for security, and ZTNA enables you to generate and manage detailed activity logs for auditing purposes.
Benefits of ZTNA
Here are six advantages of introducing ZTNA into your network security strategy:
1. Reduce Your Access Points
ZTNA communicates with the solution provider's access points. Because ports like corporate VPN gateways are not exposed externally, there are fewer points for cyber criminals to attack. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
2. Mitigate Damage
If a user terminal is infected with malware, the hacker can only access authorized resources, preventing secondary damage.
3. Security Regardless of Location
Security is applied network-wide to maintain a constant level of protection, regardless of where employees are accessing the network from.
4. Supports Remote Work
When employees work away from the office, they communicate with cloud-based access points provided by service providers. This makes distributed access easier, thereby preventing delays from interfering with productivity.
5. Scalability and Reduced Management
Because ZTNA is controlled by software, it is easy to deploy and expand as your organization changes. Additionally, your administrators can consolidate the IT workload to core operations to reduce server and network device management.
6. Manage Security Policies Centrally
ZTNA lets you manage security policies centrally and apply changes network-wide, ensuring efficient risk management and improved safety.
Secure Your Network With ZTNA From Safous
ZTNA is becoming the standard for network protection, especially as more businesses adapt hybrid and remote work models. Not only does ZTNA protect companies from rising cyber attacks, it also delivers more flexibility and efficiency than traditional network security.
Are you ready to see what ZTNA can do for your business? Safous’ advanced ZTNA lets your team connect easily and securely, with 24/7 monitoring. Request a demo to see our user-friendly ZTNA in action, or contact us anytime to learn more how Safous can keep your network safer than ever.
Receive the latest news, events, webcasts and special offers!
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Blog: Zero Trust vs. Legacy Security Systems: What’s the Right Choice?

Blog: How is ZTNA different from SASE?





